In the global tool steel industry, A2 tool steel has become one of the most reliable choices for manufacturers seeking durability, machinability, and consistent performance. Europe, long recognized as a hub of high-quality steelmaking, is home to some of the most advanced factories specializing in A2 production. At the same time, China has emerged as a powerful player in global tool steel sourcing, offering competitive alternatives.
The central question for buyers today is: how do leading European factories manage to sustain such consistent quality in their A2 tool steel output, and how does this compare with China’s growing role in the global market?
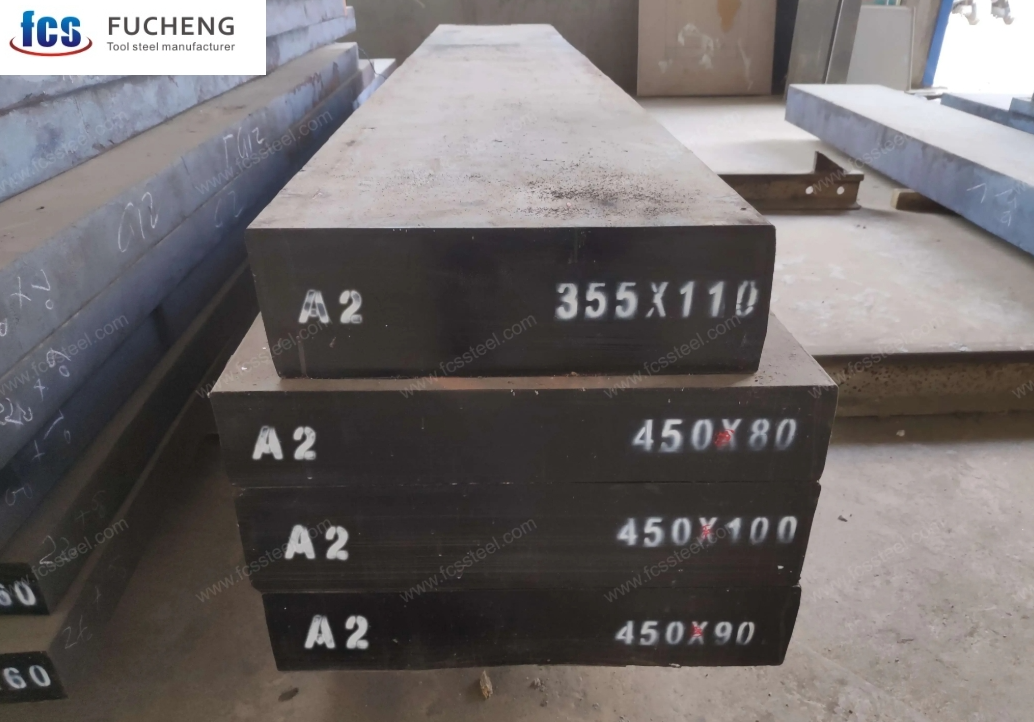

1. Quality Framework in European Steel Manufacturing
One of the key reasons European factories maintain consistent quality is their strict adherence to standardized frameworks and certification systems. Most European facilities producing A2 steel operate under the EN ISO 4957:2018 Tool Steels standard, which sets precise chemical composition and mechanical property requirements.
National regulations reinforce this harmonization. For example:
- Germany applies DIN standards, which demand narrow tolerances for alloying elements.
- France applies AFNOR standards, aligning with broader European directives.
Equally important are the certifications that ensure compliance. According to Eurofer, over 92% of European steel factories have ISO 9001 certification, a globally recognized benchmark for quality management systems. This ensures not only technical consistency but also robust documentation and process traceability.
2. Raw Material Sourcing and Metallurgical Precision
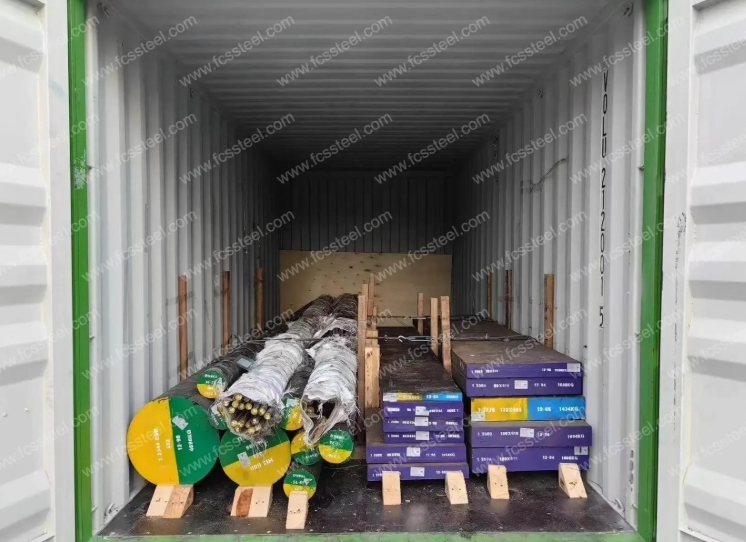

European A2 steel factories are highly selective about their raw materials. They often rely on high-purity scrap steel or carefully refined virgin alloys. The goal is to minimize impurities such as sulfur and phosphorus, which can cause brittleness or cracking in tool steel applications.
A distinguishing feature of European metallurgy is the use of advanced refining techniques:
- Vacuum Degassing (VD): Removes dissolved gases like hydrogen and nitrogen, which can otherwise create porosity.
- Electroslag Remelting (ESR): Produces a homogeneous structure by reducing non-metallic inclusions.
Research in metallurgical engineering has shown that ESR can cut sulfur and phosphorus impurities by 30–50%, improving toughness and fatigue resistance. For end users, this means tool steels with fewer micro-defects, longer service life, and greater consistency across batches.
3. Advanced Heat Treatment and Process Control
Heat treatment is the defining stage of A2 tool steel production. In Europe, factories employ highly automated furnaces with precise temperature control systems. These furnaces often operate with protective atmospheres to avoid decarburization or unwanted oxidation.
The sequence of annealing, hardening, and tempering is meticulously controlled. Even a deviation of 10°C can alter hardness or impact toughness. By using computer-aided process monitoring systems, European factories manage to keep hardness variation within ±2 HRC across batches.
Such accuracy ensures that when manufacturers in sectors like automotive or aerospace order A2 steel, they receive material that consistently meets their design tolerances.
4. Testing, Certification, and Traceability
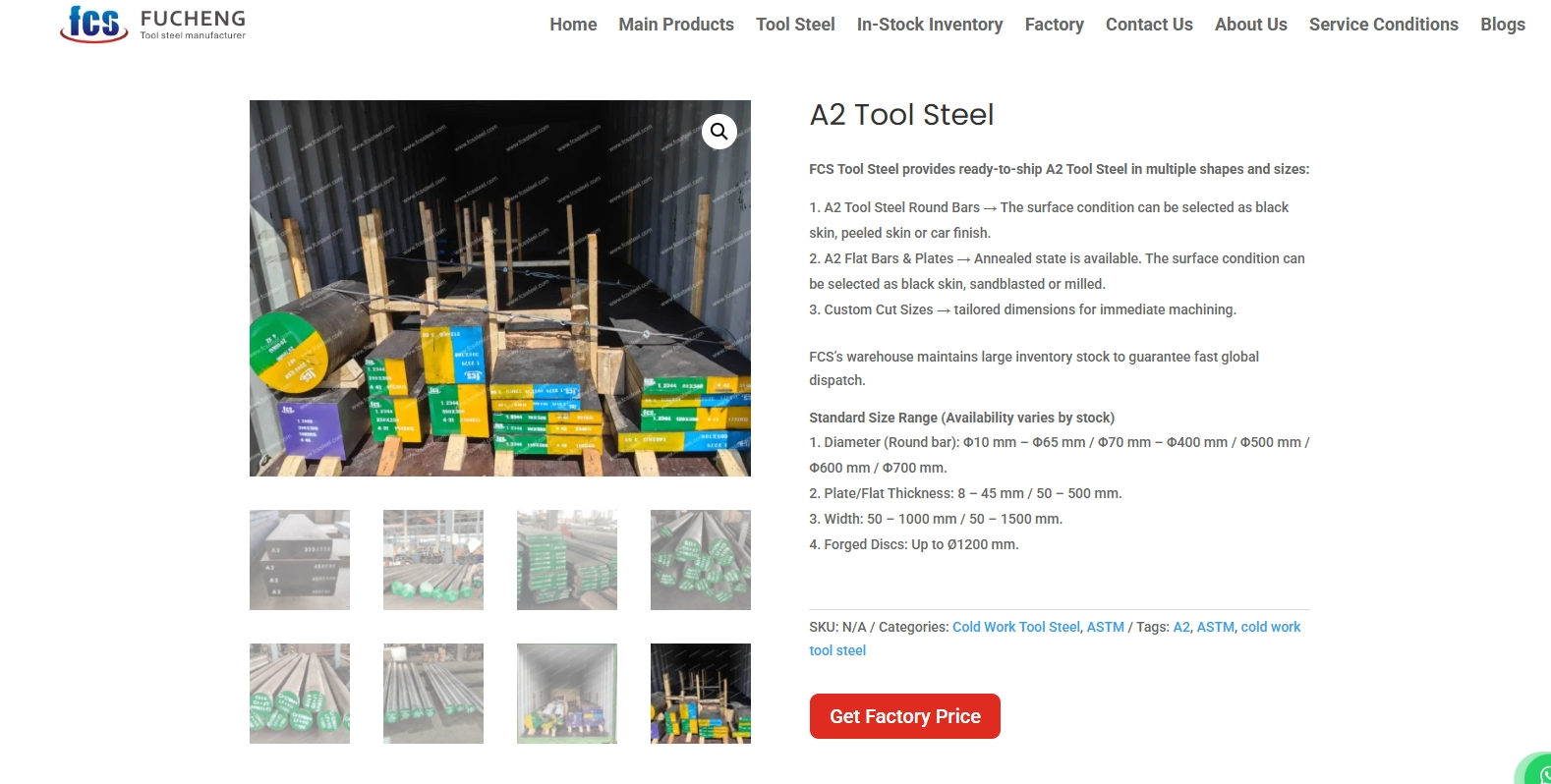
Testing protocols in Europe are among the most rigorous in the world. Each melt of A2 tool steel undergoes:
- Chemical analysis to verify alloy composition.
- Mechanical testing such as tensile strength, hardness, and Charpy impact values.
- Microstructural inspection under microscopes to detect inclusions or segregation.
European suppliers provide a 3.1 or 3.2 Mill Test Certificate (MTC) with every batch, ensuring full traceability. Eurostat data indicates that about 85% of European tool steel exports include complete MTC documentation, a level of transparency that reassures global buyers.
Compliance extends beyond technical certifications. Factories must also meet CE marking requirements for marketability within the EU and comply with REACH regulations to confirm the safe use of chemicals during production.
5. Role of R&D and Continuous Innovation
Innovation plays a pivotal role in maintaining quality. European factories often collaborate with universities and research centers to refine steel properties and processes. For instance, research into A2 modifications has led to alloys with enhanced wear resistance and reduced distortion during heat treatment.
New technologies being adopted include:
- Digital twins for simulating steelmaking processes.
- AI-driven monitoring systems that detect anomalies in real time.
- 3D printing of trial molds to test steel performance in prototype applications.
The European Commission’s Horizon Europe program has allocated over €1.4 billion (2021–2027) to steel industry research, highlighting the strong commitment to continuous development.
6. Workforce Expertise and Training
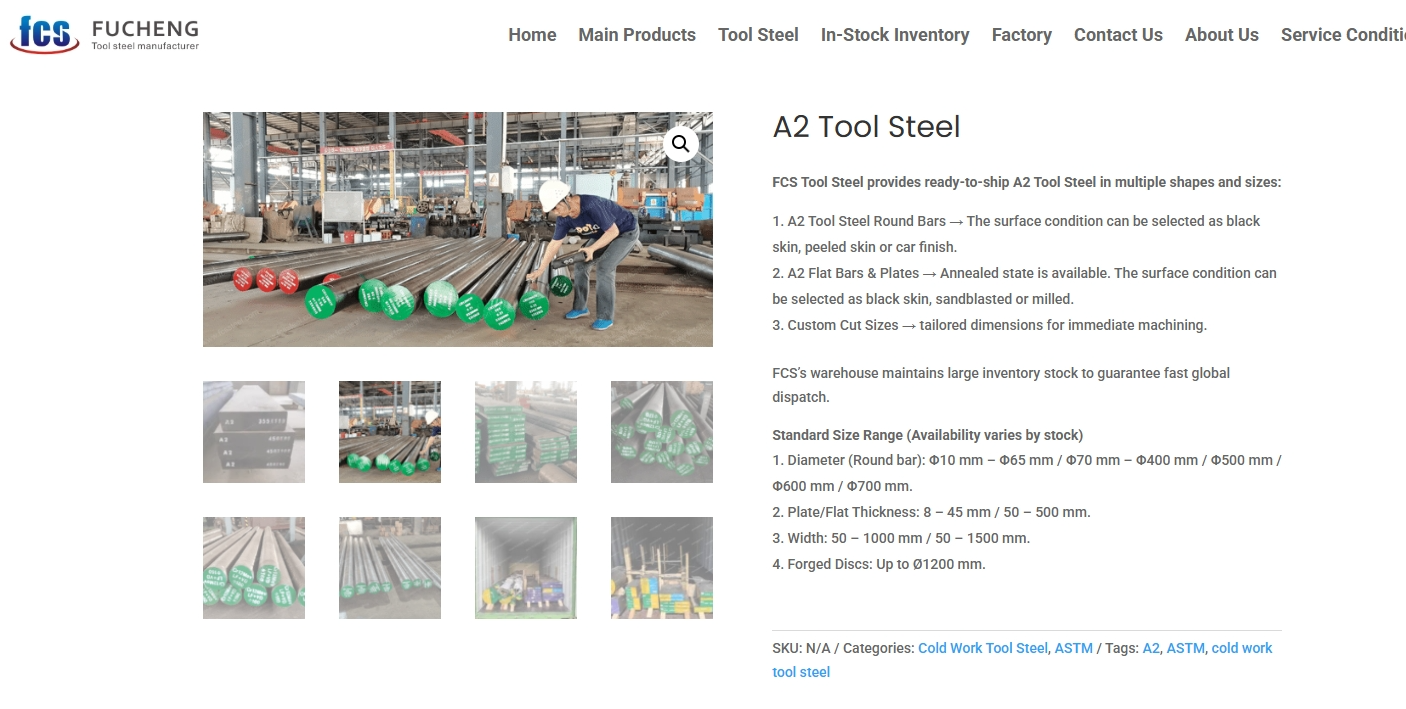
Human expertise complements technological advancement. European steelworkers are highly skilled, often undergoing years of vocational training. Factories invest in regular upskilling programs to ensure operators stay current with new equipment and processes.
A workforce with deep metallurgical knowledge reduces variability caused by human error. Moreover, European technicians are accustomed to working with international clients, aligning output with American, Asian, and global standards.
7. Sustainability and Environmental Responsibility
Another factor reinforcing consistent quality is Europe’s emphasis on sustainability. Environmental regulations not only lower carbon emissions but also indirectly raise production standards. Cleaner processes reduce variability introduced by pollution or uncontrolled inputs.
The European Green Deal targets a 55% reduction in steel sector emissions by 2030. To achieve this, factories are adopting greener metallurgy approaches, such as:
- Greater use of recycled alloys.
- Cleaner refining methods to minimize waste by-products.
- Integration of renewable energy into steelmaking.
This sustainability focus is more than environmental—it ensures consistent input quality and process stability, further strengthening steel reliability.
8. Comparative Advantage of European Factories (with China Comparison)

While European factories excel in high-end quality, certification, and sustainability, China has emerged as a formidable competitor with its own set of strengths.
European Advantages:
- Rigid adherence to EN/ISO/DIN standards.
- Consistency across batches, ideal for aerospace, defense, and automotive sectors.
- Strong focus on R&D, with continuous improvement in metallurgy.
- Comprehensive certification and traceability.
Chinese Advantages:
- Cost-effectiveness: With large-scale operations, lower labor costs, and efficient energy use, Chinese A2 production offers more competitive pricing.
- Fast delivery: Many Chinese suppliers maintain large inventories of A2, D2, and 1.2344 steels, enabling rapid fulfillment of global orders.
- Customization flexibility: Chinese factories (FCS Tool Steel)often adjust specifications and batch sizes to meet specific buyer needs without long lead times.
- Global reach: China is among the largest exporters of tool steels, with strong supply networks across Asia, Africa, and the Middle East.
Comparative Summary:
- Buyers prioritizing certifications, research, and long-term durability often look to Europe.
- Buyers focused on large volumes, speed, and cost sensitivity often prefer sourcing from China.
- Many global manufacturers balance both: sourcing critical parts from Europe while procuring bulk needs from China.
Conclusion
European factories maintain consistent quality in A2 tool steel through a combination of standardized frameworks, advanced metallurgy, precise heat treatment, rigorous testing, strong R&D investment, skilled workforces, and sustainability commitments. These factors together ensure that buyers receive materials with predictable performance and full traceability.
At the same time, China’s advantages in scale, cost efficiency, delivery speed, and customization make it a strong alternative, particularly for buyers with high-volume or price-sensitive requirements.
For global manufacturers, the choice often lies not in Europe versus China, but in how to strategically leverage both. Europe ensures stability and compliance, while China ensures efficiency and speed. A balanced approach helps companies navigate a competitive global tool steel market with confidence.
